Definition of Fistula:
Fistula is defined as an abnormal tract lined by epithelium,endothelium,granulation tissue or fibrous tissue connecting two epithelial surfaces either in between the exterior and an internal viscus(External fistula) or in between two internal viscera(Internal fistula).Classification:
A.Congenital:
- Bronchial fistula(neck,lower 1/3rd)
- Tracheo-oesophageal fistula
B.Acquired:
- Fistula-in-ano
- Arteriovenous fistula-Hemodialysis,Trauma
- Neoplastic
- Rectovaginal fistula
- Gastrocolic fistula
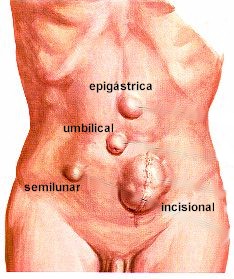
 |
| Anorectal fistulas |
Clinical features of Sinus/Fistula:
1.Persistent or intermittent discharge from an abnormal opening.2.intermittent swelling and pain of the local site followed by discharge and relief of pain.
3.Symptoms of underlying pathology,e.g.,
a)TB
- Low grade fever
- Cough
- Haemoptysis
- Chest pain
- Dyspnoea
From birth,e.g.,Preauricular sinus
c)Osteomyelitis(OM)
- High fever
- Pain
- Swelling of the bone concerned
History of ischiorectal abscess
Causes of persistence of a sinus:
1.Presence of FB or necrotic tissue- Suture material
- Sequestrum(Necrotic tissue and foreign body)
- Bullet
- Pellet
- Worms
3.Abscess of rest for
- Fistula in ano(Proximal colostomy is done)
5.When the tract is lined by epithelium or endothelium
6.When the tract contains excessive fibrous tissue(prevents collapsing) around the tract(e.g.,Chronic empyema chest)
7.Naturre of infection
- TB
- Actinomycosis
9.Persistent discharge(VVF-urine)
10.Chronic illness or systemic illness
- DM
12.Nutritional deficiency
13.Drugs
- Steroid
- RVF in treating carcinoma of cervix
Principle of Treatment of Sinus/Fistula:
1.Excision followed by biopsy2.Treatment of the underlying cause(e.g., TB,DM,Carcinoma,Malnutrition)